
Cotesia marginiventris (Creson)
(Insecta: Hymenoptera: Braconidae)
As generalists, Cotesia spp. parasitoids are recorded on many common agricultural pests including armyworms, cutworms, diamondback moth, and Helicoverpa zea (known as corn earworm, cotton bollworm, and tomato fruitworm). Cotesia marginiventris also is used as a biological control of beet armyworm and cabbage looper.
Cotesia marginiventris adults are approximately 3 mm long. A good sign of the parasitoid’s presence is a caterpillar that is empty inside, but the cuticle layer is intact and one round exit hole is visible.
Cotesia marginiventris lays its eggs into young larvae of noctuid moths. The developing parasitoid consumes the internal tissues of the host and completes its life cycle in approximately 13 days.
Cotesia marginiventris is native to the West Indies and is present in Florida.
Images
To save the Web-optimized images shown below to your hard drive:
PC users: right click to "Save Picture (or Image) As..."
Mac users: click and drag to your desktop.

Adult
Cotesia
marginiventris
(Creson) on a corn leaf with host larvae
(Photographer:
Andrei
Sourakov, Florida
Museum of Natural History)
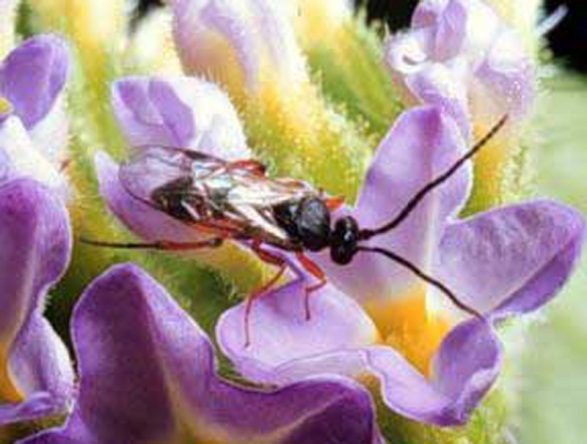

Adult
male Cotesia
marginiventris
(Creson)
(Photographer:
Andrei
Sourakov, Florida
Museum of Natural History)

Larva
of Cotesia
marginiventris
(Creson)
(Photographer:
Andrei
Sourakov, Florida
Museum of Natural History)
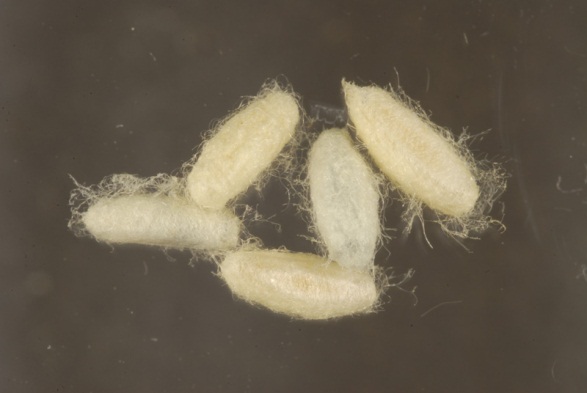
Pupae
of Cotesia
marginiventris
(Creson)
(Photographer:
Lyle
Buss, University of Florida)

Exit
hole (on right) caused by emergence of Cotesia
marginiventris
(Creson) from dead host larva
(Photographer:
Andrei
Sourakov, Florida
Museum of Natural History)