common name: Asian subterranean termite
scientific name: Coptotermes gestroi (= havilandi) (Wasmann) (Insecta: Blattodea: Rhinotermitidae)
Introduction - Distribution - Description and Identification - Life History - Damage - Pest Status - Management - Selected References
Introduction (Back to Top)
Kirton and Brown (2003) determined that "Haviland's subterranean termite," Coptotermes havilandi Holmgren, was a newer second name given to a termite that already had the name Coptotermes gestroi (Wasmann). By proper taxonomic convention, the older name, Coptotermes gestroi, must be recognized. They also proposed that Coptotermes gestroi be given the common name of "Asian subterranean termite." Coptotermes gestroi is a very damaging termite and a threat to wooden structures wherever it occurs. As one might expect, Coptotermes gestroi is similar in many respects to Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki, the Formosan subterranean termite. General information related to the life history, damage, and management of Coptotermes formosanus is applicable to Coptotermes gestroi and can be obtained from our sister publication on Coptotermes formosanus. This report highlights the known distribution and important distinguishing characteristics of Coptotermes gestroi.
Figure 1. Formosan subterranean termite, Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki, soldier showing the ovoid head shape and large fontanelle that are characteristic of all Coptotermes species. Photograph by Rudolf H. Scheffrahn, University of Florida.
Distribution (Back to Top)
Coptotermes gestroi is endemic to Southeast Asia. Over the last century, human activity has spread this termite species far beyond its native range. It was collected in the Marquesas Islands (Pacific Ocean) in 1932, and Mauritius and Reunion (Indian Ocean) in 1936 and 1957, respectively. In the New World tropics, this species was first reported in Brazil in 1923 and in Barbados in 1937. Recent collections from other West Indian islands include Antigua, Barbuda, Cuba, Grand Cayman, Grand Turk, Jamaica (Montego Bay and Port Antonio), Little Cayman, Montserrat, Nevis, Providenciales, Puerto Rico (San Juan), St. Kitts, and on a boat from the U.S. Virgin Islands. It has also been collected in southern Mexico.
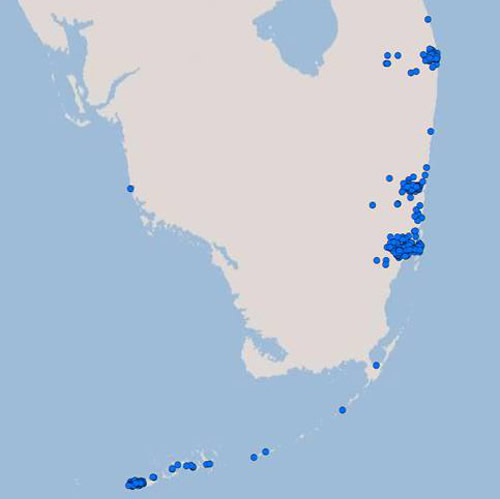
Figure 2. Distribution of the Asian subterranean termite. Coptotermes gestroi (= havilandi) (Wasmann). Map by John Warner, University of Florida
In 1996, Coptotermes gestroi was collected for the first time in the continental United States from a storefront and a church in Miami, Florida (Su et al. 1997). In 1999, a colony of Coptotermes gestroi was discovered infesting a waterfront house in Key West, Florida. In 2001 a single alate was collected in Lauderhill, Broward County, Florida. As of 2004, six structures in Key West have been verifiably infested with Coptotermes gestroi. A boat moored off Fleming Key and in drydock on Stock Island (east of Key West) was also infested. Broward and Dade are the only known counties where Coptotermes formosanus and Coptotermes gestroi have both become established. Elsewhere in the world, these two widely introduced species are geographically isolated. Coptotermes formosanus usually invades mildly temperate climates (to 35 degrees north latitude in the U.S.), while Coptotermes gestroi is limited to more tropical localities (to 26 degrees north) as noted above. In the West Indies, Coptotermes gestroi has invaded some natural woodland habitats. In Florida, it has been collected only from structures, ornamental trees near structures, and boats. Three private boats in Florida have been found with shipboard infestations, one arriving from Jamaica, one from Virgin Gorda, and one from Providenciales. These boats were docked in Ft. Pierce, Hollywood, and Ft. Lauderdale, respectively. Shipboard infestations are the most likely means of human dispersal of this pest as the result of on-board dispersal flights that reach land.
In early 2005, Coptotermes gestroi was found in the cities of Ft. Lauderdale and Riviera Beach (adjacent to the north of West Palm Beach). These discoveries are new records for established, land-based colonies of this species in Palm Beach and Broward Counties. The Riviera Beach infestations mark a substantial northward range expansion for this species in Florida and are the northernmost established colonies of this tropical species worldwide. The presence of mature Coptotermes gestroi colonies in these areas significantly increases the overlap in south Florida between this tropical termite and the closely related Formosan subterranean termite, Coptotermes formosanus, a more temperate species. Currently, this is the only known location in the world where the two species occur together (sympatry).
Description and Identification (Back to Top)
Superficially, soldiers of Coptotermes gestroi resemble those of Coptotermes formosanus. Both species have a large opening on the forehead called the fontanelle. When viewed from above, both also share tear drop-shaped heads. Microscopic examination of the fine hairs on the head reveals diagnostic differences. Coptotermes gestroi soldiers have one pair of hairs near the rim of the fontanelle, while in Coptotermes formosanus, two pairs originate around the fontanelle. Additionally, the lateral profile of the top of the head just behind the fontanelle shows a weak bulge in Coptotermes gestroi that is absent in Coptotermes formosanus. As with Coptotermes formosanus, Coptotermes gestroi soldiers constitute about 10 to 15 percent of foraging groups, aggressively bite when challenged, and exude a white mucous-like secretion from the fontanelle.
Figure 3. Lateral view of soldier head capsules of Coptotermes gestroi (Wasmann) (left) and Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki. Antennae removed for clarity. Photograph by Rudolf H. Scheffrahn, University of Florida.
The alates of Coptotermes gestroi are slightly smaller than those of Coptotermes formosanus (total length with wings about 13-14 mm vs.14-15 mm, and maximum head width 1.4 mm vs. 1.5 mm, respectively). The head, pronotum, and dorsal abdomen of Coptotermes gestroi alates are dark brown, while those of Coptotermes formosanus are entirely a lighter yellow-brown or orange-brown. The darker pigmentation of the Coptotermes gestroi head provides a contrasting background for two light patches on the face called antennal spots. In Coptotermes formosanus the antennal spots are barely, if at all, visible. The length of wing hairs is somewhat shorter in Coptotermes gestroi than in Coptotermes formosanus.
Figure 4. Alate head capsules of Coptotermes gestroi (Wasmann) (left) and Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki. Antennae partially removed for clarity. Photograph by Rudolf H. Scheffrahn, University of Florida.
Figure 5. Coptotermes gestroi (Wasmann) wing (inset shows close-up of hairs on wing membrane). Photograph by Rudolf H. Scheffrahn, University of Florida.
Figure 6. Coptotermes gestroi (Wasmann) alate. Photograph by Rudolf H. Scheffrahn, University of Florida.
Life History (Back to Top)
Like Coptotermes formosanus, Coptotermes gestroi dispersal flights or "swarms" occur at dusk or at night in which large numbers of alates leave the colony. A flight of Coptotermes gestroi occurred in a Key West hotel room on 10 February 2004 at 1:30 AM. The hotel occupants reported that they and their belongings were covered with alates and many had crawled into their luggage and clothing. In Florida and the West Indies, Coptotermes gestroi flights have been record between February and April. The Coptotermes gestroi flight season ends about when the Coptotermes formosanus flight-season begins. Porch lights, indoor lights, and video monitors often attract the alates inside, especially when doors and unscreened windows are opened. When large numbers (100s-1,000s) of alates are found indoors, their presence is usually indicative of a structural infestation as noted above. Alates flying indoors are unlikely to find the moist wood/soil substrate they need for successful colonization, and succumb quickly to desiccation. It is likely, however, that most dispersal flights will produce a few new colonies that may become a damage threat in future years.
Figure 7. Coptotermes gestroi (Wasmann) alate (top) and dealate. Photograph by Rudolf H. Scheffrahn, University of Florida.
Damage (Back to Top)
Like other structure-infesting species of Coptotermes, damage resulting from a Coptotermes gestroi infestation can become severe in a relatively short time, especially when a structure is invaded by a large, mature colony. Dispersal flights, foraging tubes, or damage are usually the first indications of an infestation. Advanced stages of infestation are indicated by the incorporation of nest material (carton) in hollowed wood or existing structural voids.
Figure 8. Damage by Coptotermes gestroi (Wasmann) to fascia, Grand Turk Island. Photograph by Rudolf H. Scheffrahn, University of Florida.
Figure 9. Damage by Coptotermes gestroi (Wasmann) to church pew, Miami. Photograph by B. Maharajh.
Figure 10. Carton material in door casing damaged by Coptotermes gestroi (Wasmann), Key West. Photograph by Mark Lang.
Figure 11. Foraging tube made with coral sand by Coptotermes gestroi (Wasmann), Key West. Photograph by Mark Lang.
Pest Status (Back to Top)
Infestations of Coptotermes gestroi in Florida are becoming more common in recent years and will continue. Due to climatic restrictions, the future distribution of Coptotermes gestroi in the continental United States will probably not extend far beyond southern Florida. The importance of this pest is likely to increase in the West Indies and it may surface in other tropical regions in years to come.
Management (Back to Top)
The same management strategies such as baits and soil treatments employed for Coptotermes formosanus should be considered for Coptotermes gestroi.
Selected References (Back to Top)
- Cabrera BJ, Su N-Y, Scheffrahn R. (2005). UF/IFAS researchers find another termite in south Florida as destructive as Formosan "super termite." UF/IFAS News. http://news.ifas.ufl.edu/story.aspx?id=955 (18 February 2009).
- Kirton LG, Brown VK. 2003. The taxonomic status of pest species of Coptotermes in Southeast Asia: Resolving the paradox in the pest status of the termites, Coptotermes gestroi, C. havilandi and C. travians (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Sociobiology 42: 43-63.
- Scheffrahn RH, Su N-Y, Diehl B. 1990. Native, introduced, and structure-infesting termites of the Turks and Caicos Islands, B.W.I. (Isoptera: Kalotermitidae, Rhinotermitidae, Termitidae). Florida Entomolologist 73: 622-627.
- Scheffrahn RH, Su N-Y. (March 2000). Current distribution of the Formosan subterranean termite and Coptotermes havilandi in Florida UF/IFAS. http://www.ftld.ufl.edu/bbv3n1.htm#termite (April 2000).
- Su N-Y, Ban PM, Scheffrahn RH. 2000. Control of Coptotermes havilandi (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) with hexaflumuron baits and a sensor incorporated into a monitoring-baiting program. Journal of Economic Entomology 93: 415-421.
- Su N-Y, Scheffrahn RH, Weissling T. 1997. A new introduction of a subterranean termite, Coptotermes havilandi Holmgren (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in Miami, Florida. Florida Entomologist 80: 408-411.