common name: proturans
scientific name: Protura spp. (Entognatha: Protura)
Introduction - Distribution - Description - Life History - Collecting - Selected References
Introduction (Back to Top)
Protura are minute soil-inhabiting hexapods characterized by the lack of eyes and antennae, a 12-segmented abdomen, and development by anamorphosis. The first described species of Protura, Acerentomon doderoi, was published in 1907 by Silvestri.
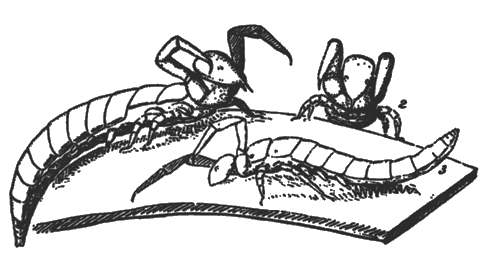
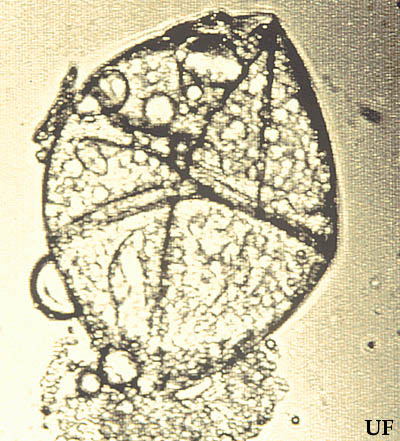
Figure 1. Early woodcut of the first published illustrations of Protura (Berlese 1907).
Little is known about the ecology of Protura, including their diet. In culture, proturans have been observed feeding on mycorrhizal fungi, dead Acari, and mushroom powder. Early taxonomic work led researchers to believe Protura were a sister group to the Collembola. Recent phylogenetic examinations revealed very large differences between proturans and the insect orders. Once considered insects, proturans are now listed as an order in the class Entognatha, though Protura may also be a separate class. Presently, there are over 500 species described within nine families (two suborders) found worldwide (Tipping 2008).
Distribution (Back to Top)
Proturans are found world-wide primarily inhabiting soil, leaf litter, moss, and decaying wood. They have also been collected in animal burrows, meadows, and agriculture soils. One researcher has even collected proturans from the grassy margins of a Chicago freeway.
A single proturan species was reported from Orlando, Florida by Ewing in 1940, Acerentulus floridanus. Undoubtedly, other species, both novel and previously described, will be found in Florida with further investigations of the soil biota.
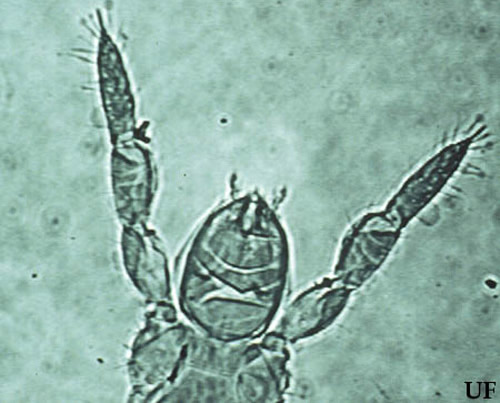
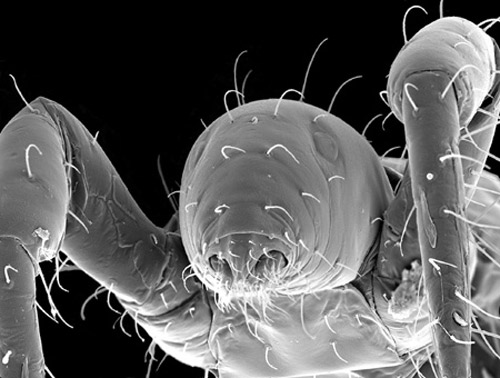
Figure 2. Prothoracic legs, head and thorax of the proturan Eosentomon maryae Tipping, (300x). Photograph by Christopher Tipping, University of Florida.
Description (Back to Top)
Protura are divided into two suborders: Eosentomoidea and Acerentomoidea. Members of Eosentomoidea possess meso and metathoracic spiracles with a primitive tracheal system, while proturans within Acerentomoidea lack these structures. Proturans have small appendages ventral on the first three abdominal segments. Mouthparts are entognathous and are greatly modified between genera.
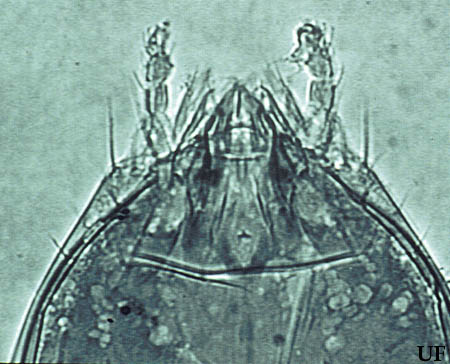
Figure 3. Photomicrograph of the head of Eosentomon megatibiense Tipping, with mouthparts inserted inside of the head capsule (900x). Photograph by Christopher Tipping, University of Florida.
Click here to see a video of a proturan walking (3.6 MB). Video by Christopher Tipping, University of Florida
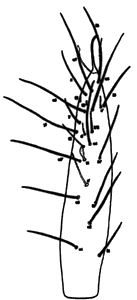
The first pair of legs are used as antennae and have many tarsal sensilla and sensory hairs.
Figure 4. Foretarsi of Eosentomon maryae Tipping with sensilla and setal patterns. Drawing by Christopher Tipping.
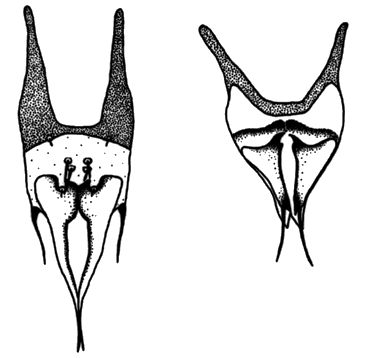
The internal genitalia (squama genitalis) are sclerotized with anterior basal apodemes. Genital opening is between the eleventh segment and the telson.
Figure 5. Squamma genitalis of Eosentomon caddoense Tipping; male left, female right. Drawing by Christopher Tipping.
Figure 6. Frontal view of an acerentomid proturan. Photograph by Dr David E. Walter, University of Queensland, Australia.
Figure 7. Lateral view of an acerentomid proturan. Photograph by Dr David E. Walter, University of Queensland, Australia.
Life History (Back to Top)
Unique among hexapods, Protura exhibit anamorphosis, i.e., the larvae hatch with a few abdominal segments with the number increasing with subsequent moults. The embryology is unknown. All proturans have five distinct stages. One family, Acerentomidae, has six. The eggs of only a few species have been recorded.
Figure 8. Egg of proturan from the family Eosentomidae (1200x). Photograph by Christopher Tipping, University of Florida.
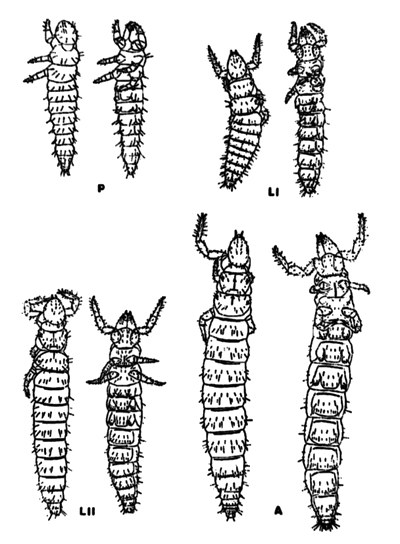
The prelarva is hatched with nine abdominal segments and weakly developed mouthparts. Larva I also has nine abdominal segments with fully developed mouthparts. Larva II is the third stage and has an additional segment added between the telson and the eighth. Maturus junior is the next stage and exhibits 12 abdominal segments. The maturus junior moults to the adult except for males in the family Acerentomidae, which have another stage known as the pre-imago. This stage displays partially developed genitalia. It is not known if the adult continues to moult throughout its life.
Figure 9. Proturan life stages. P=prelarva, L1=larva I, LII=larva II, A=adult.
Click here to see a video of a proturan exhibiting defensive posture (2.0 MB). Video by Christopher Tipping, University of Florida.
Collecting (Back to Top)
Proturans are easily collected with Berlese-type funnels. Deeper soil forms can be collected by the centrifugation sugar flotation technique. Material should be stored in 75 to 80% ethanol until permanent slides can be made. Various mounting media have been used to clear and preserve specimens, including Swan's, Hoyer's and balsam.
Selected References (Back to Top)
- Berlese A. 1907. Monografia dei Myrientomata. Redia 6: 1-82.
- Copeland TP. 1964. New species of Protura from Tennessee. Journal of the Tennessee Academy of Science 39: 17-29.
- Copeland TP, Imadate G. 1990. In Soil Biology Guide. Dindall DL (ed.). Wiley Press, New York. Chapter 29, 911-933.
- Ewing HE. 1940. The Protura of North America. Annals of the Entomological Society of America 33: 495-551.
- Jenkins WR. 1964. A rapid centrification-flotation technique for separating nematodes from the soil. Plant Distribution Report 48: 692.
- Nosek J. 1973. The European Protura. Mus. D'Hist. Naturelle, Geneva. 345 pp.
- Tipping C. 2008. Proturans (Protura). pp. 3062-3064. In Encyclopedia of Entomology, Vol. 3, Capinera JL (editor). Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
- Tipping C, Allen RT. 1994. Description of two new species of Eosentomon from the Ouachita Mountains of Arkansas (Protura: Eosentomidae). Journal of the Kansas Entomological Society 67: 253-266.
- Tipping C, Allen RT. 1995. Description of two new species of Eosentomon with a key to the species with the 6/4 setal pattern on sterna IX/X (Protura: Eosentomidae). Journal of the New York Entomological Society 103: 287-301.
- Tuxen SL. 1964. The Protura. Paris: Herman. 360 pp.