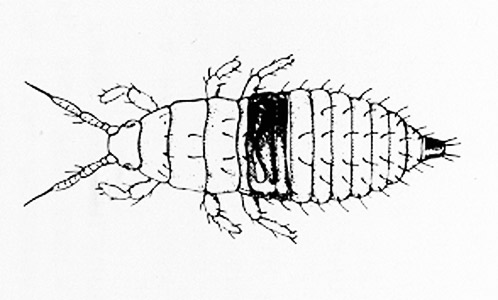
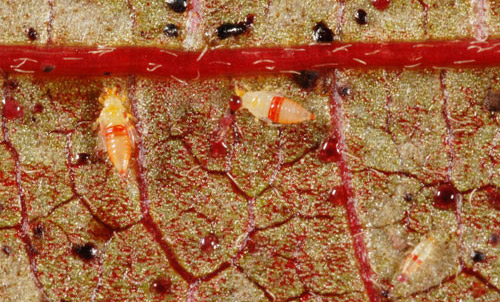
common name: redbanded thrips
scientific name: Selenothrips rubrocinctus (Giard) (Insects: Thysanoptera: Thripidae)
Introduction - Synonymy - Distribution - Description and Life Cycle - Hosts - Economic Importance - Management - Selected References
Introduction (Back to Top)
The redbanded thrips, Selenothrips rubrocinctus (Giard), was first described from Guadeloupe, West Indies, where it was causing considerable damage to cacao. As a result, it was referred to as the cacao or cocoa thrips. The earliest report relating to this thrips was a report by W.E. Broadway in 1898, when he called attention to the "blight" of cacao.
Figure 1. Redbanded thrips adult. Drawing by Division of Plant Industry.
Synonymy (Back to Top)
Heliothrips rubrocinctus Giard
Physopus rubrocinctus Giard (1901)
Heliothrips (Selenothrips) decolor Karny
Heliothrips (Selenothrips) mendex Schmutz
Brachyurothrips indicus Bagnall
(from Forestry Compendium)
Distribution (Back to Top)
The redbanded thrips is a tropical-subtropical species thought to have originated in northern South America (Chin and Brown 2008) and is found in the following areas:
- Asia — China, Malaya, Philippine Islands, Taiwan;
- Africa — Bioko, Ghana, Ivory Coast, Nigeria, Principe Island, Sierra Leone, Tanzania, Uganda, Zaire;
- Australasia and Pacific Islands — Hawaiian Islands, Mariana Islands, New Caledonia, New Guinea, Papua, and Solomon Islands;
- North America — United States (Florida), Mexico;
- Central America — Costa Rica, Honduras, Panama;
- West Indies;
- South America — Brazil, Ecuador, Guiana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela.
In Florida, this species is found from Key West to Macclenny (Baker County in north Florida), but more generally it is found from the Orlando area south.
Description and Life Cycle (Back to Top)
The female is about 1.2 mm in length and has a dark brown to black body underlain by red pigment chiefly in the first three abdominal segments; the anal segments retain a reddish black color, and the wings are dark. The male is similar, but smaller and is seldom collected.
Figure 2. Adult redbanded thrips, Selenothrips rubrocinctus (Giard). Photograph by Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida.
The nymph and pupa are light yellow to orange with the first three and last segments of the abdomen bright red. After hatching, there are two nymphal stages lasting nine to ten days. Fully-grown second stage nymphs are about 1 mm long. The two nymphal stages are followed by two resting stages (pre-pupal and pupal stages). The resting stages last three to five days before adults emerge (Chin and Brown 2008).
Figure 3. Redbanded thrips, Selenothrips rubrocinctus (Giard), nymph. Drawing by Division of Plant Industry.
Figure 4. Immature redbanded thrips, Selenothrips rubrocinctus (Giard), and excrement pellets. Photograph by Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida.
Figure 5. Pupae of redbanded thrips, Selenothrips rubrocinctus (Giard). Photograph by Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida.
Eggs are inserted into the lower leaf surface and covered with a drop of fluid, which dries to form a black, disc-like cover (Astridge and Fay 2005). Females lay up to 50 eggs and live for up to one month. The eggs hatch within four days (Chin and Brown 2008). In Florida, the life cycle is completed in about three weeks, and there are several generations a year.
Hosts (Back to Top)
The redbanded thrips is a pest of many plants. The locality and its flora usually determine the more prevalent hosts. In the West Indies, it has been a serious pest of cacao and mango. The species of tropical fruit trees, ornamentals and shade trees that it attacks are too numerous to list. The favorite tropical fruit hosts in Florida are mango and avocado. It has also been a problem in sweetgum trees in central Florida.
Economic Importance (Back to Top)
The larvae and adults feed on the foliage and the fruit by piercing the epidermis with their mouthparts. Redbanded thrips prefer young foliage and their feeding causes leaf silvering, distortion, leaf drop. The thrips destroys the cells on which it feeds, causes injury to the fruit, and leaves unsightly dark colored droplets or blotches of excrement on the leaf surface. A more serious injury is leaf drop, which may denude trees. Honeydew excretory products from red-banded thrips and other insect infestations fall to leaves, fruits or objects beneath, giving rise to the objectionable fruit-degrading, black sooty mold.
Figure 6. Typical thrips damage. Photograph by James L. Castner, University of Florida.
Figure 7. Typical thrips damage, with immature redbanded thrips, Selenothrips rubrocinctus (Giard). Photograph by Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida.
Management (Back to Top)
Redbanded thrips are preyed upon by a large assortment of natural predators such as spiders, mites, lacewings, predatory thrips, and predatory bugs, especially minute pirate bugs (Chin and Brown 2008, Funderburk et al. 2000).
Chemical controls are not always necessary for this thrips, as natural controls are apparently effective most of the time. However, if chemical control is required, consult the Vegetable Production Handbook of Florida.
Selected References (Back to Top)
- Astridge D, Fay H. (2005). Red-banded thrips in rare fruit. Department of Primary Industries and Fisheries, Queensland. (no longer available online)
- Dennill GB. 1992. Orius thripoborus (Anthocoridae), a potential biocontrol agent of Heliothrips haemorrhoidalis and Selenothrips rubrocinctus (Thripidae) on avocado fruits in the eastern Transvaal. Journal of the Entomological Society of Southern Africa 55: 255-258.
- Fennah RG. 1965. The influence of environmental stress on the cacao tree in predetermining the feeding sites of cacao thrips, Selenothrips rubrocinctus (Giard), on leaves and pods. Bulletin of Entomological Research 56: 333.
- Funderburk J, Diffie S, Sharma J, Hodges A, Osborne L. (2007). Thrips of ornamentals in the southeastern U.S. EDIS. (18 February 2019)
- Giard A. 1901. Sur un thrips (Physopus rubrocinctus nov. sp.) nuisible au cacaoyer. Bulletin de la Societe Entomologique de France 15: 263-265.
- Hecht O. 1952. Nota acerca de Selenothrips rubrocinctus Giard, playa del cacaotero. Fitofilo San Jacinto DF. Mexico. An. 6, N. 5: 33-42.
- Moritz G, Morris DC, Mound LA. 2001. Thrips ID: an interactive identification and information system (CD), Pest thrips of the world. CSIRO Publishing, Collingwood, Australia.
- Reyne A. 1921. De cacaothrips (Heliothrips rubrocinctus Giard). Suriname Dept. v.d. Landbouw Bull. 44. 214 pp.
- Russell HM. 1912. The red-banded thrips. Papers on insects injurious to citrus and other subtropical fruits. USDA Bureau of Entomology Bulletin 99: 17-29.
- Wang WX. 1984. Bionomics and control of Selenothrips rubrocinctus. Acta Entomologica Sinica 27: 81-86.